How Does a Gas Boiler Heat Exchanger Work?
Gas boilers are especially created for home heating and offer efficient heating of one’s place, thus helping to save much energy, time and money. These are beneficial opportunities for those people, who live in harsher and colder climates, where autumn and winter seasons are rather severe.
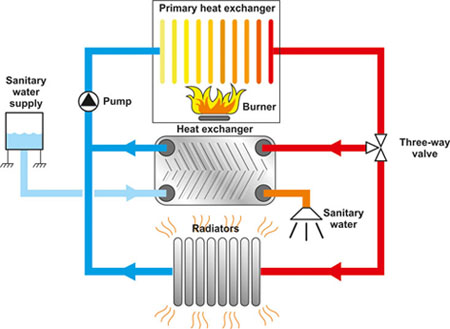
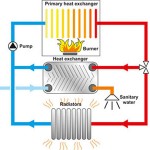
The key elements of an ordinary gas boiler are:
- burner
- heat exchanger
- exhaust stack
- controls
- combustion chamber
Gas boiler heat exchanger enables heat transfer from one source to another over a solid surface. If we speak about a condensing type, here the process includes the heat from fuel gases that is used for heating water that is returning from radiators to the boiler. So, a condensing boiler does not have to work really hard or use too much fuel for getting the water up to the temperature that is required for heating the house.
Usually a gas boiler heat exchanger is fitted around the fuel that comes from the boiler for heating up main cold water that is into it. The liquid is either used as pre-heating incoming water or is stored in a tank for a later use.
The Heat Exchanger Repair
In case the exchanger is cracked, there will be water spilling onto the floor. It flows through the exchanger, when heated and before directed to the baseboard heating sources or the radiators. When there is a crack, the liquid seeps out of this crack right onto the floor.
Sometimes heat exchangers with a very small crack do not leak water onto the floor. However, the problem is that they can leak it onto the burner, which is used to heat the water flowing through the pipes. If the liquid drops down right onto the burner, it extinguishes the fire. When the fire is out, the burner is no longer heating the water and there won’t be any heat coming from baseboard heating sources or radiators.
Heat Exchangers in Standard and Condensing Models
If we speak of a standard gas boiler, it should be noted that it has a maximum energy efficiency that equals 83% only. This is possible due to the fact fuel gases are discharged at temperatures above 60°C. The cooling requires the use of a special gas boiler heat exchanger – a stainless steel one, as the steel won’t corrode, being in contact with the condensed gases.
In a conventional model, the fuel is burned and hot gases that are produced are passed through a heat exchanger. This is where much of the heat is transferred to water, raising the liquid’s temperature.
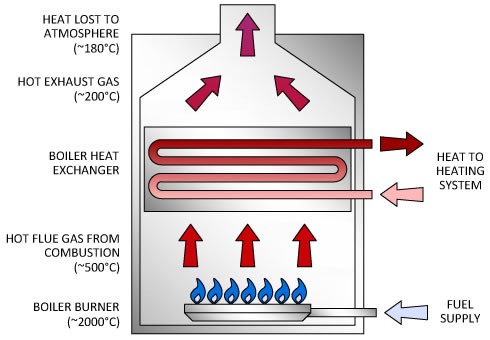
When there is a condensing boiler, the model has a comparatively more efficient heat exchanger that extracts the maximum quantity of heat from the burned gas. Condensing models can use either a power burner or an aspirating burner that has an induced draft fan. In addition they have a heat exchanger that is made of corrosion-resistant materials. This exchanger extracts latent heat that remains in the combustion products, condensing before the products are exhausted. As a chimney isn’t needed, installation costs are low.
After the fuel is burned, the hot gases produced pass through a gas boiler heat exchanger and then transfer to water, thus increasing its temperature.
- popular
- new